Calibration Requirement Score F mount |
The Calibration Requirement information shows the typical required calibration across all F mount lenses on the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests there is statistically less need to calibrate the autofocus, although as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras it is still common to require calibration even on generally excellent cameras.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Median Adjustment | 1.4 units |
| Typical Adjustment (Worst 50%) | 2.7 units |
| Requiring Visually Significant Adjustment (4 or more units) | 16.2% |
Calibration Requirement
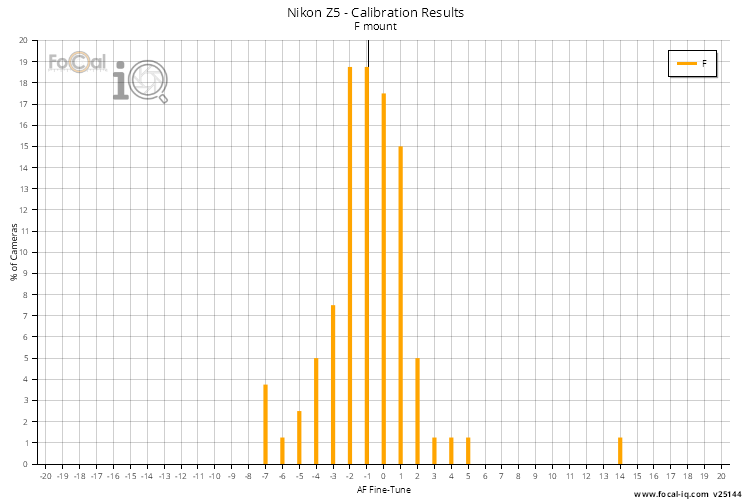
The histogram below shows the frequency of calibration results from all FoCal calibration tests run on the Nikon Z5 with F mount lenses.
The value along the horizontal axis shows the amount of focus adjustment, and the height of the line at each point shows what percentage of cameras require this adjustment.
A perfect camera would have a single bar at 0 on the horizontal axis reaching 100%, indicating that all examples of this camera require no calibration.
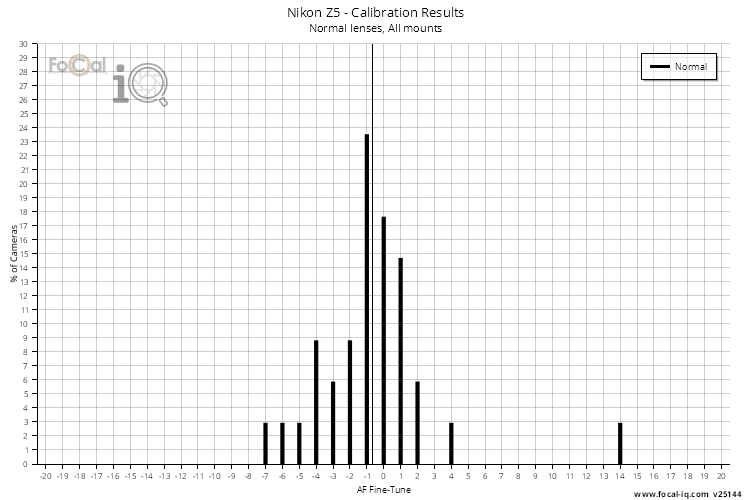
Calibration Requirement by Focal Length
The chart below shows the results from all FoCal calibration tests run on this camera split by focal length groups.
Ultrawide is under 24mm, Wide is under 35mm, Normal is under 60mm, Telephoto is under 300mm and Super Telephoto is over 300mm.
Calibration Range Score F mount |
The Calibration Range information shows the spread of typical required calibration across all F mount lenses on the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests there is statistically less need to calibrate the autofocus, although as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras it is still common to require calibration even on generally excellent cameras.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Adjustment Range of top 50% | +2.7 units |
| Requiring Visually Significant Adjustment (4 or more units) | 16.2% |
Calibration Range
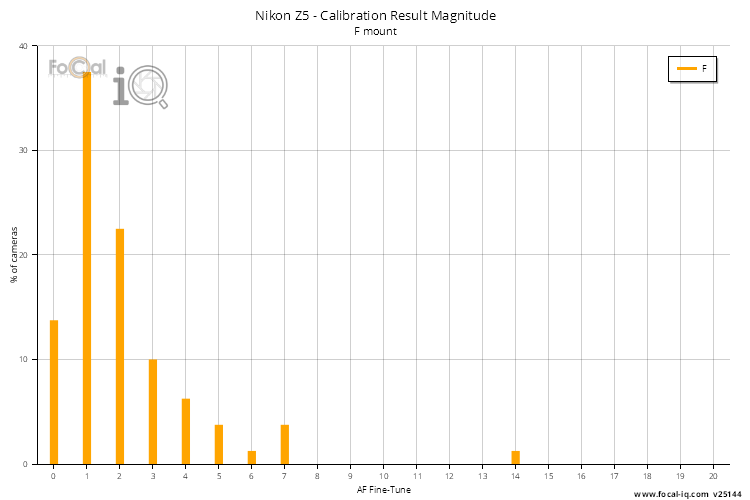
The following table shows the range of Focus Adjustment values for the best 50% of tests on this camera across all lenses. If you were to buy two Nikon Z5 cameras, it is statistically likely that one of them will require more than the adjustment shown below.
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Adjustment Range of top 50% | +2.7 units |
| Top 50% Adjustment Limits | -2.3 to +0.4 |
The following table shows the percentage of cameras requiring no focus adjustment, a small adjustment (less than 2 focus adjustment units), or a significant adjustment (2 or more focus adjustment units) that will definitely start to impact image quality.
Focus Consistency Score F mount |
The Focus Consistency information shows the repeatability of focus operations for F mount lenses on the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests the camera autofocus system behaves consistently, although as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras, this does not mean that every example of this camera will behave the same.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Calibrated Consistency of Focus | 99.4% |
| Consistency of Focus (Live View) | 99.6% |
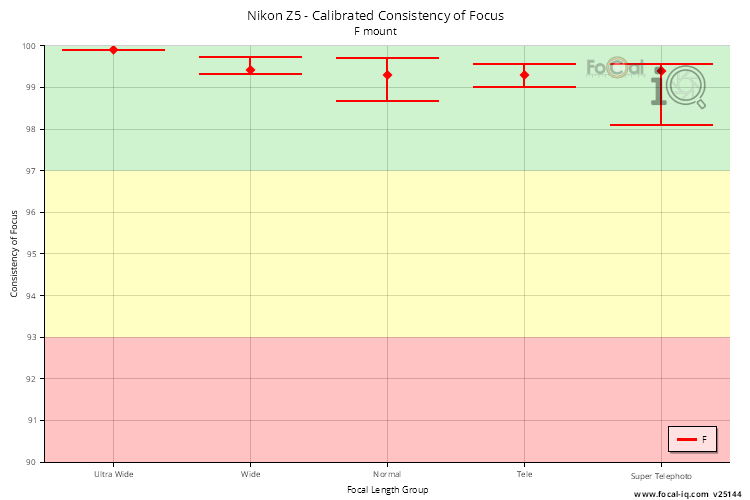
Calibrated Consistency of Focus
The following data is derived from the variation in image quality for repeated focus operations with a defocus step in between. The data shown here uses only points very close to the best calibration results for the lens. For the Nikon Z5, the focus method used would be Image Sensor (Hybrid AF or Contrast Detect AF).
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Ultra Wide | 99.9% (0.7%) |
| Wide | 99.4% (10.1%) |
| Normal | 99.3% (13.8%) |
| Tele | 99.3% (28.3%) |
| Super Telephoto | 99.4% (5.1%) |
Live View Consistency of Focus
The data for Live View Consistency of Focus is derived from the AF Consistency test and the CalCheck tool.
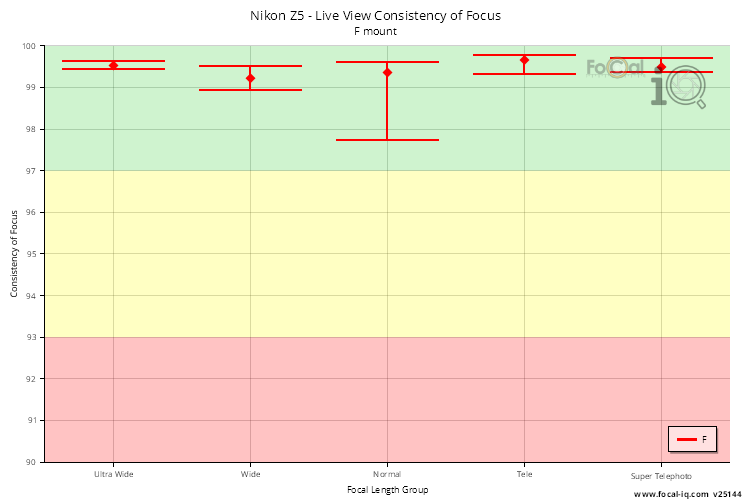
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Ultra Wide | 99.5% (3.8%) |
| Wide | 99.2% (3.8%) |
| Normal | 99.4% (15.4%) |
| Tele | 99.7% (21.2%) |
| Super Telephoto | 99.5% (5.8%) |
Focus Accuracy Score F mount |
The Focus Accuracy information shows the variability of focus operations for F mount lenses on the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests the focus accuracy is very good, altough as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras, this does not mean that every example of this camera will behave the same.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Representative Focus Accuracy | +0.9 units |
The overall focus accuracy metric is determined by looking at the variation of quality values during calibration testing, and using the overall calibration profile to calculate the number of focus adjustment units of variation that each shot exhibited.
A perfect camera and lens would focus on exactly the same spot each time a focus operation was performed, leading to a focus error of zero.
Below is the typical focus error across all F mount lenses on the Nikon Z5 - the gauge shows the score for this value, with a lower focus error meaning better focus performance and leading to a higher score.
F mount
Focus Error across Focal Lengths
The following table shows the typical focus error split between focal length groups.
Ultrawide is under 24mm, Wide is under 35mm, Normal is under 60mm, Telephoto is under 300mm and Super Telephoto is over 300mm.
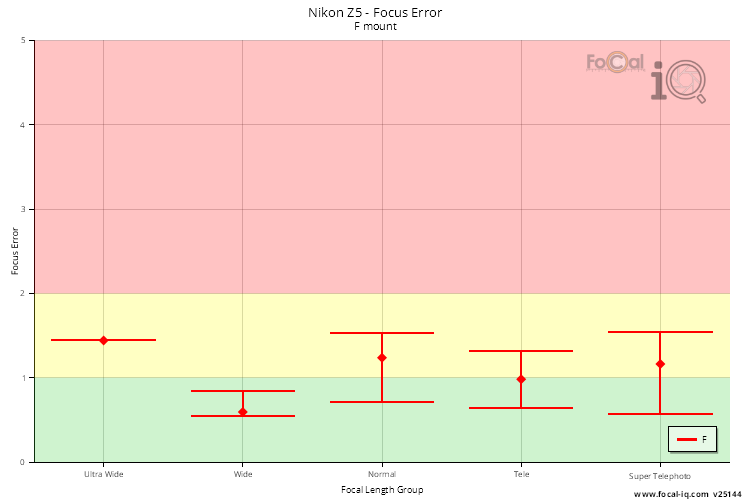
| F Mount | |
|---|---|
| Ultra Wide | 1.4 units (0.8%) |
| Wide | 0.6 units (9.8%) |
| Normal | 1.2 units (13.5%) |
| Tele | 1.0 units (27.8%) |
| Super Telephoto | 1.2 units (5.3%) |
The Stabilisation information shows how the image stabilisation system works for F mount lenses on the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests the stabilisation system of the camera performs well, although as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras, this does not mean that every example of this camera will behave the same.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
The data below is shown for the following data sets:
All Lenses
The following data is for all lenses (i.e. those with stabilisation like IS, VR etc, and those without). That data is shown for each mount.
Handheld Stops Improvement (All Lenses)
This chart shows the improvement in stops accumulated for all lenses attached to the Nikon Z5.
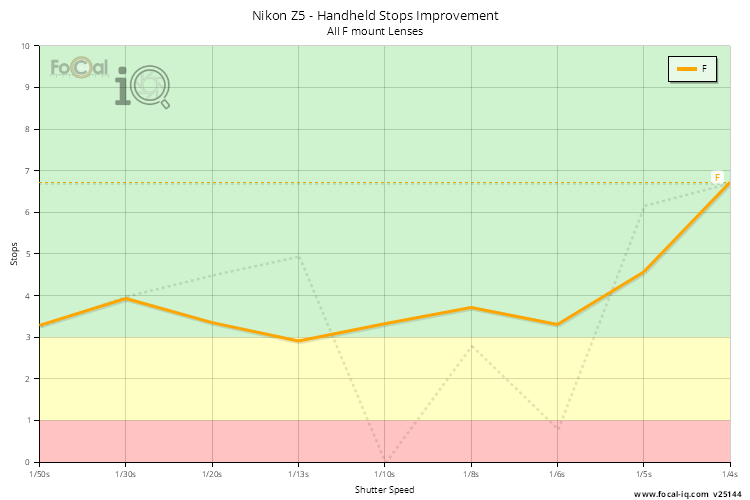
The data is calculated for individual FoCal Stabilisation Tests by finding the shutter speeds with matching quality levels when stabilisation is both active and disabled. For FoCal IQ we then combine all the data across the shutter speed range, then average the data from unique cameras (so a single camera cannot heavily influence the results irrespective of the number of tests performed).
Handheld Quality Difference (All Lenses)
The Handheld Quality Difference chart shown below graphs the quality difference between a handheld shot with the stabilisation system active and inactive for each shutter speed.
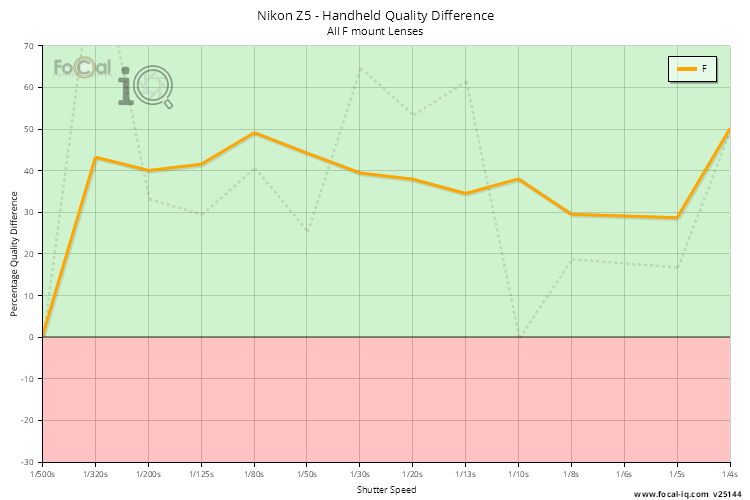
A value above 0 (in the green area of the chart) shows an improvement in quality when the image stabilisation system is active. If the image quality is degraded with the stabilisation system active, the point will have a value lower than zero and be shown in the red area.
The data is calculated from all Stabilisation Test results - we accumulate all the data for the various shutter speeds, average data for individual cameras (so a single user is represented with one data point irrespective of how many tests they perform) and then present the data below.
The thick line shows averaged results to smooth out any jaggedness from the raw data (which is shown by the faint dotted line).
Tripod Quality Difference (All Lenses)
The Tripod Quality Difference chart shown below graphs the quality difference between a tripod-mounted shot with the stabilisation system active and inactive for each shutter speed.
A value above 0 (in the green area of the chart) shows an improvement in quality when the image stabilisation system is active. If the image quality is degraded with the stabilisation system active, the point will have a value lower than zero and be shown in the red area.
The data is calculated from all Stabilisation Test results - we accumulate all the data for the various shutter speeds, average data for individual cameras (so a single user is represented with one data point irrespective of how many tests they perform) and then present the data below.
The thick line shows averaged results to smooth out any jaggedness from the raw data (which is shown by the faint dotted line).
Non-Stabilised Lenses
The following data is for lenses that don't have any stabilisation (e.g. VR, IS, OS etc) attached to the Nikon Z5 - all stabilisation performance is gained purely by the in-body stabilisation system of the camera.
Handheld Stops Improvement (Non-Stabilised Lenses)
This chart shows the improvement in stops accumulated for all lenses attached to the Nikon Z5.
The data is calculated for individual FoCal Stabilisation Tests by finding the shutter speeds with matching quality levels when stabilisation is both active and disabled. For FoCal IQ we then combine all the data across the shutter speed range, then average the data from unique cameras (so a single camera cannot heavily influence the results irrespective of the number of tests performed).
Handheld Quality Difference (Non-Stabilised Lenses)
The Handheld Quality Difference chart shown below graphs the quality difference between a handheld shot with the stabilisation system active and inactive for each shutter speed.
A value above 0 (in the green area of the chart) shows an improvement in quality when the image stabilisation system is active. If the image quality is degraded with the stabilisation system active, the point will have a value lower than zero and be shown in the red area.
The data is calculated from all Stabilisation Test results - we accumulate all the data for the various shutter speeds, average data for individual cameras (so a single user is represented with one data point irrespective of how many tests they perform) and then present the data below.
The thick line shows averaged results to smooth out any jaggedness from the raw data (which is shown by the faint dotted line).
Tripod Quality Difference (Non-Stabilised Lenses)
The Tripod Quality Difference chart shown below graphs the quality difference between a tripod-mounted shot with the stabilisation system active and inactive for each shutter speed.
A value above 0 (in the green area of the chart) shows an improvement in quality when the image stabilisation system is active. If the image quality is degraded with the stabilisation system active, the point will have a value lower than zero and be shown in the red area.
The data is calculated from all Stabilisation Test results - we accumulate all the data for the various shutter speeds, average data for individual cameras (so a single user is represented with one data point irrespective of how many tests they perform) and then present the data below.
The thick line shows averaged results to smooth out any jaggedness from the raw data (which is shown by the faint dotted line).
Stabilised Lenses
The following data is for lenses that have their own stabilisation (e.g. VR, IS, OS etc) attached to the Nikon Z5. The performance information below relates to how the camera decides to use the combination of it's internal in-body stabilisation and the lens stabilisation.
Handheld Stops Improvement (Stabilised Lenses)
This chart shows the improvement in stops accumulated for all lenses attached to the Nikon Z5.
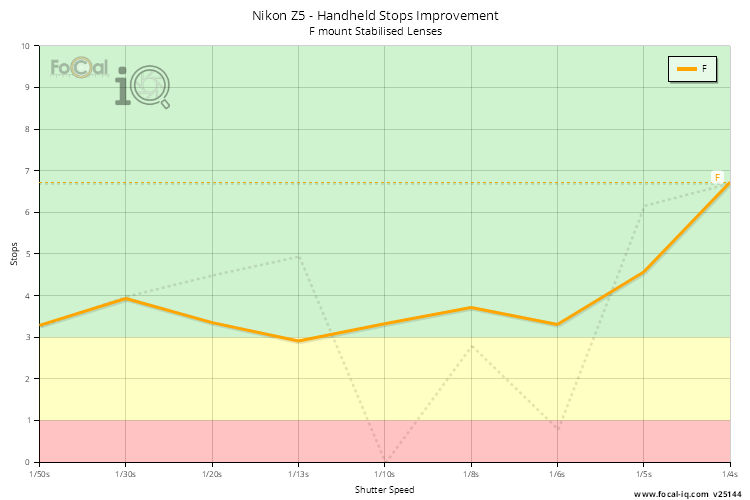
The data is calculated for individual FoCal Stabilisation Tests by finding the shutter speeds with matching quality levels when stabilisation is both active and disabled. For FoCal IQ we then combine all the data across the shutter speed range, then average the data from unique cameras (so a single camera cannot heavily influence the results irrespective of the number of tests performed).
Handheld Quality Difference (Stabilised Lenses)
The Handheld Quality Difference chart shown below graphs the quality difference between a handheld shot with the stabilisation system active and inactive for each shutter speed.
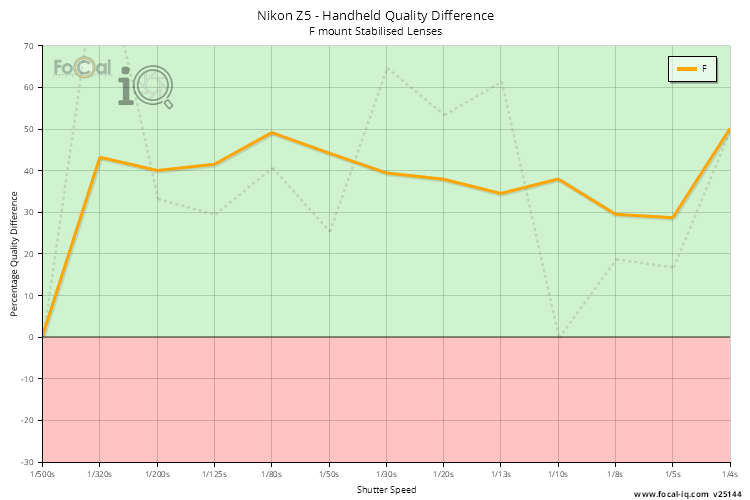
A value above 0 (in the green area of the chart) shows an improvement in quality when the image stabilisation system is active. If the image quality is degraded with the stabilisation system active, the point will have a value lower than zero and be shown in the red area.
The data is calculated from all Stabilisation Test results - we accumulate all the data for the various shutter speeds, average data for individual cameras (so a single user is represented with one data point irrespective of how many tests they perform) and then present the data below.
The thick line shows averaged results to smooth out any jaggedness from the raw data (which is shown by the faint dotted line).
Tripod Quality Difference (Stabilised Lenses)
The Tripod Quality Difference chart shown below graphs the quality difference between a tripod-mounted shot with the stabilisation system active and inactive for each shutter speed.
A value above 0 (in the green area of the chart) shows an improvement in quality when the image stabilisation system is active. If the image quality is degraded with the stabilisation system active, the point will have a value lower than zero and be shown in the red area.
The data is calculated from all Stabilisation Test results - we accumulate all the data for the various shutter speeds, average data for individual cameras (so a single user is represented with one data point irrespective of how many tests they perform) and then present the data below.
The thick line shows averaged results to smooth out any jaggedness from the raw data (which is shown by the faint dotted line).
Dust Score |
The Dust information shows how dust affects the sensor for the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests the camera is less affected to dust, although as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras, this does not mean that every example of this camera will behave the same.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
| All Mounts | |
|---|---|
| Widest Clean Aperture | f/3.2 |
| Typical Spot Count | 21.25 |
| Typical Spot Size | 0.13mm |
| Typical Spot Max Opacity | 4.8% |
| Typical Impact | 13.5% |
Dust Perception Factor
The Dust Perception Factor is a calculation which represents how likely you are to notice the dust spots on the sensor for typical shooting. A higher value indicates a higher likelihood of noticing the spots.
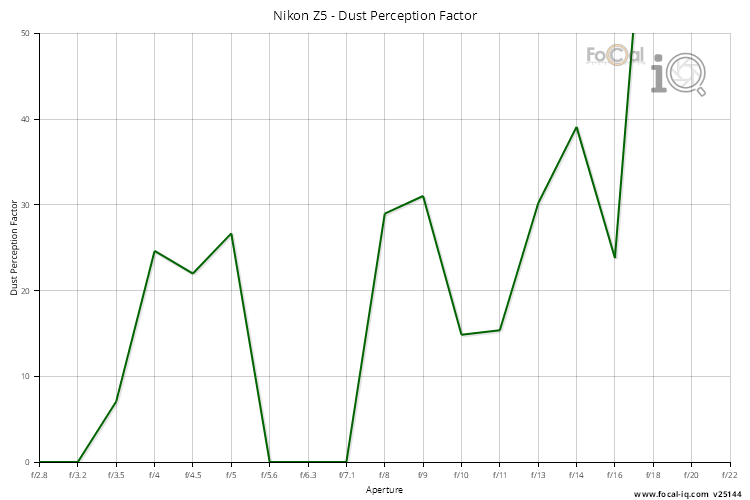
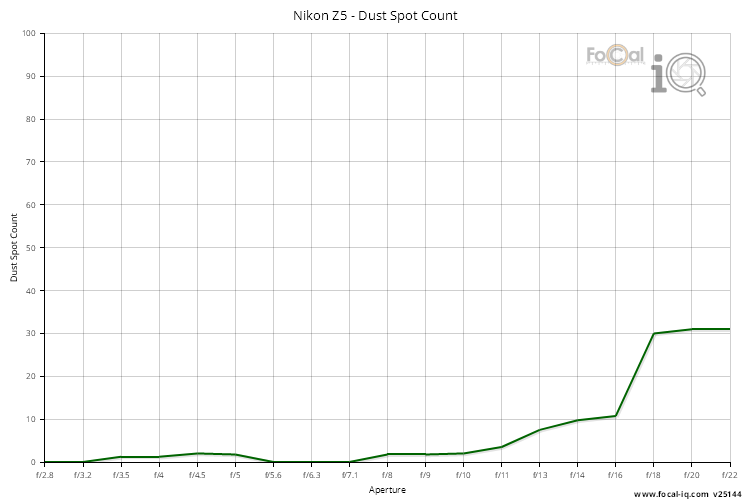
Dust Spot Count
The Dust Spot Count shows the typical number of spots found on the sensor during testing.
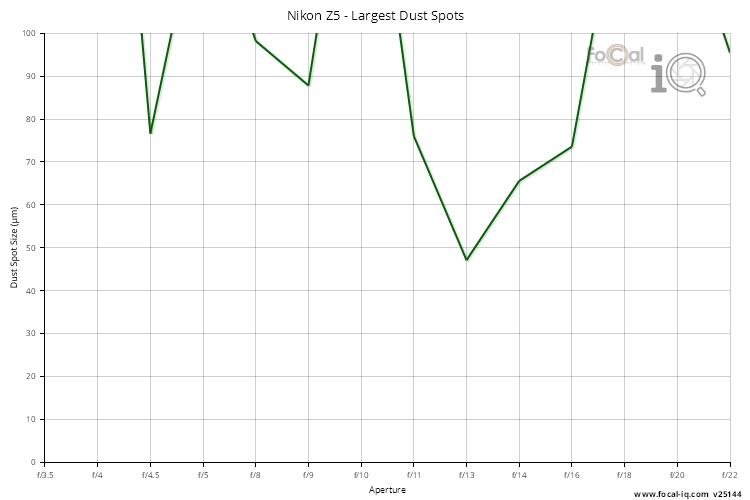
Largest Spot Size
The Largest Spot Size is the typical size (diameter in microns) of detected spots across the aperture range.
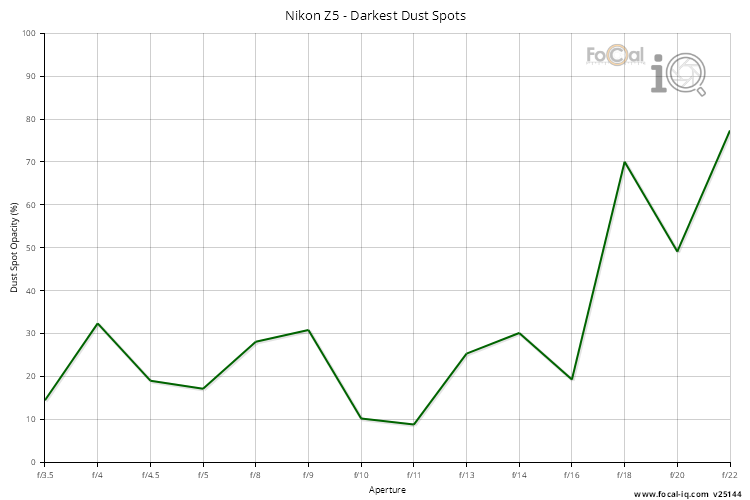
Maximum Opacity
The Maximum Opacity shows the typical opacity of the most obvious spot on the sensor.
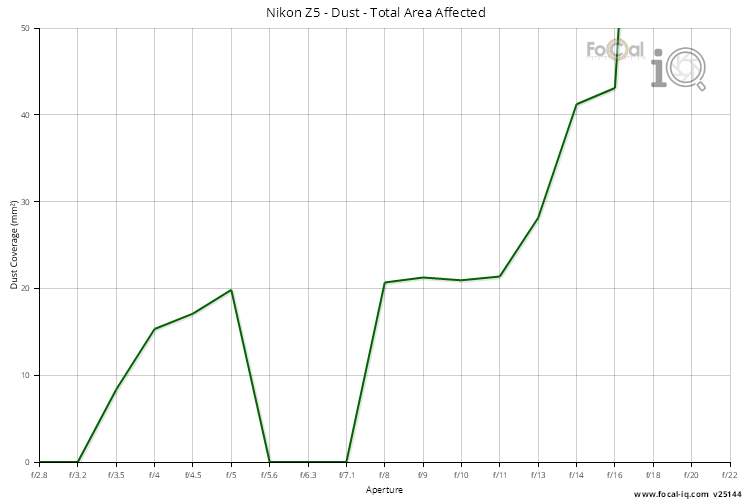
Total Area Affected
The total area affected is the typical coverage of all dust spots on the sensor.
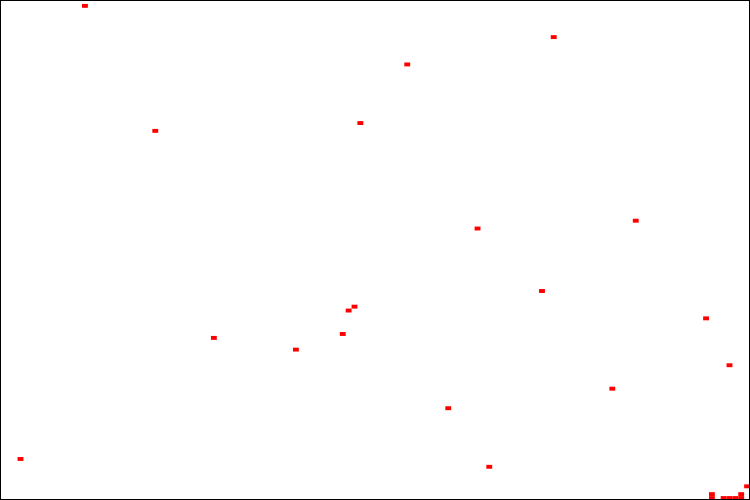
Dust Impact
The following image shows the average occurrence of dust spots on the sensor. A darker spot indicates that this area of the sensor sees more dust spots.

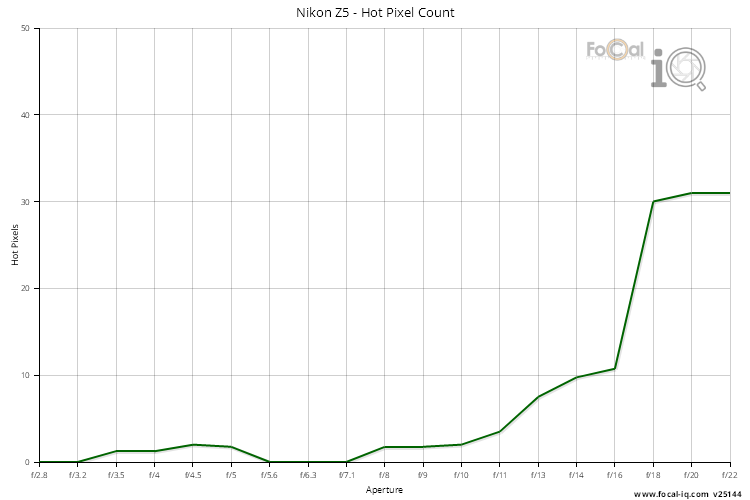
Hot Pixels Score |
The Hot Pixel information shows how hot pixels affect the sensor for the Nikon Z5.
Each metric is given a score between 0 (poor) and 100 (excellent). An overall score close to 100 suggests the camera is less affected by hot pixels, although as FoCal IQ shows a view of all cameras, this does not mean that every example of this camera will behave the same.
Summary
The following information shows the metrics used to build the overall score:
| All Mounts | |
|---|---|
| Typical Hot Pixels | 1.75 |
| Widest No Hot-pixel Aperture | f/3.2 |
Hot Pixels
The Hot Pixels chart shows the typical number of hot pixels detected at each aperture.
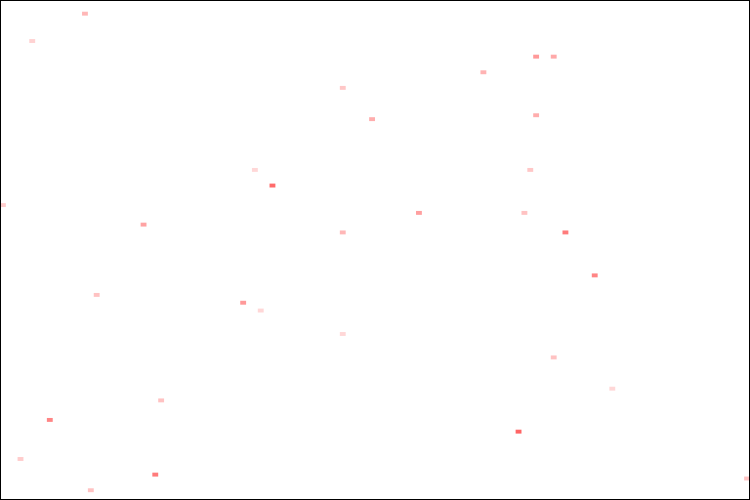
Hot Pixels
The following image shows the occurrence of hot pixels. The darker spots are detected across more apertures.
Spotted an error or have feedback about the site? Contact us